Simple UNIX Shell
A lightweight command-line shell implemented in C, designed to emulate core
functionalities of UNIX shells like sh or bash. This shell supports
process management, I/O redirection, pipelining (|), subshells,
logical operators (&&, ||), interactive input handling including
autocompletion and basic signal handling. The implementation demonstrates
system-level programming concepts using POSIX APIs.
Features
-
Command Execution
Executes external programs usingfork()andexecvp(), with environment lookup via$PATH. -
Foreground and background job execution
Commands can be run in the background by appending&. -
Redirection
Input/output redirection using<,>, and>>. Examples:cat < input.txtls > out.txtecho foo >> log.txt
-
Quoting and escape sequences
Basic support for"quoted strings"and escape sequences like\or\". -
Logical Operators
Implements support for&&and||operators, enabling conditional command execution. These operators can be combined with pipelines and subshells. -
Command separators
Supports;to execute multiple commands sequentially. -
Subshells
Commands enclosed in parentheses()are executed in subshells, enabling complex nested logic. -
Pipelines
Unix-style pipelines using the pipe (|) operator. Data is passed from one process to another via standard input/output. Example:cat file.txt | grep foo | sort -
Directory Navigation
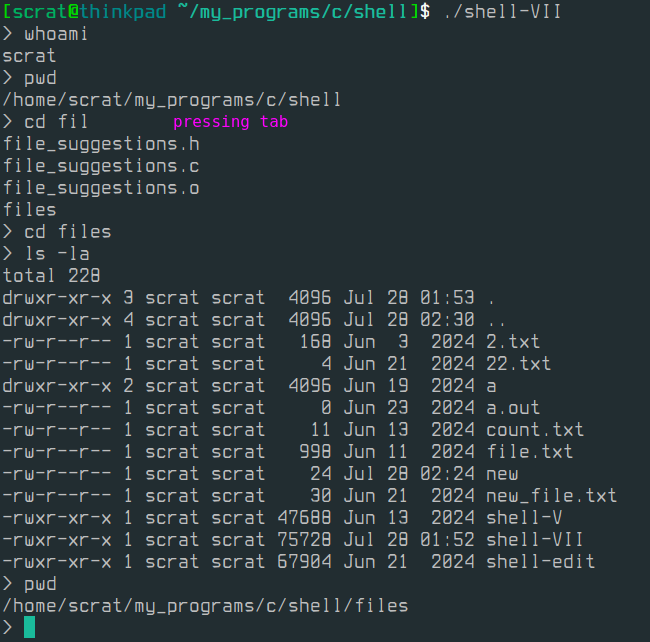
Supports the built-incdcommand to change the current working directory viachdir(). -
Autocompletion (Tab)
Custom autocompletion implemented using raw terminal input:- If the current token is a command: matches against executables in
$PATH. - Otherwise: matches file and directory names from the current or specified path.
- If the current token is a command: matches against executables in
-
Interactive Line Editing
Terminal is switched to non-canonical mode. Input handling is implemented manually:- Character-by-character input display.
- Left/right arrow keys for cursor movement.
Backspacesupport with live line re-rendering.Ctrl+Dto terminate the shell.Tabtriggers autocompletion.
-
Signal handling
Handles SIGCHLD to reap zombie processes and prevent defunct children.
Technologies Used
- Language: C (C99)
- System APIs: POSIX (
fork,execvp,waitpid,pipe,dup2,tcsetpgrp, etc.) - Memory handling: dynamic memory allocation (
malloc,free) - Terminal control:
tcgetpgrp,tcsetpgrp,tcgetattr,tcsetattr
Examples
Here are some example commands that work in this shell:
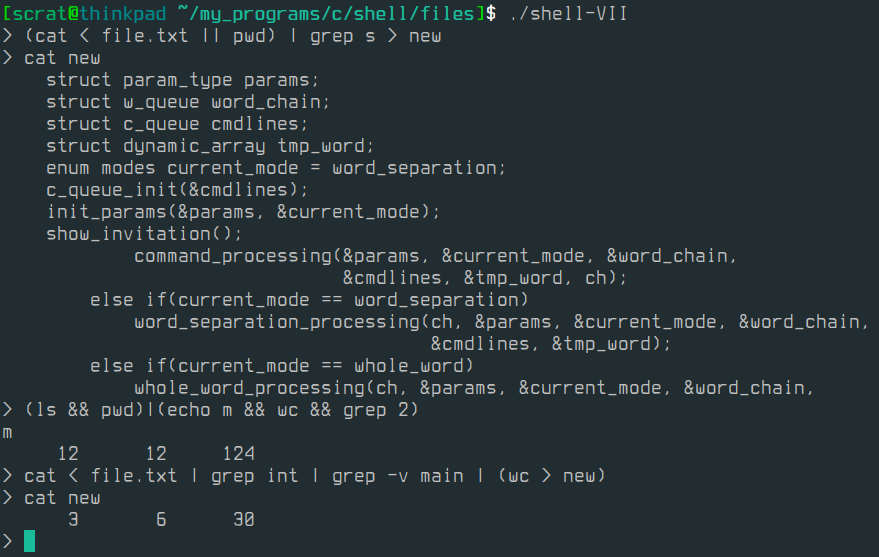
cat < file.txt & pwd
(ls && pwd) | (echo m && wc && grep 2)
cat < file.txt | grep int | grep -v main | (wc >> new)
(ls && m) && pwd
ls & yes | cat
ls & cat < file.txt
(cat < file.txt && pwd) | grep s > new
yes | cat | cat
(ls) | cat | grep
(ls && m ) & whoami
Limitations
While the shell supports many core UNIX behaviors, it has some limitations compared to full-featured shells:
- No scripting constructs (
if,while,for, etc.) - No variable expansion (e.g.
$HOME,$PATH,$?) - No command substitution (e.g.
`command`or$(command)) - No history (up arrow)
- No job control (e.g. fg, bg, jobs).
- No advanced signal features (sigaction, sigprocmask, kill, etc.).
- Test mode: Not all commands have been fully verified. Some commands may produce unexpected errors.
You’ll see a prompt where you can enter commands, use pipes, redirection, and job control. You can also interact via signals like Ctrl+C and Ctrl+Z.
